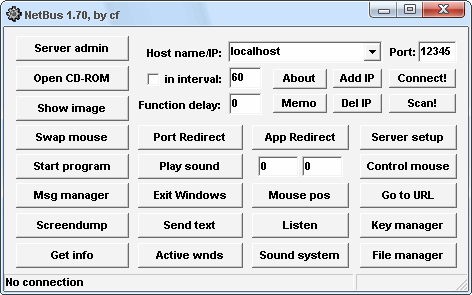
Netbus client (v1.70) works fine in Windows 2000 and in Windows XP as well. Major parts of the protocol, used between the client and server interaction (in version 1.70) are textual. Thus the server can be controlled by typing human understandable commands over a raw TCP connection. Download netbus server.exe for free. Internet & Network tools downloads - NetBus by Carl-Fredrik Neikter and many more programs are available for instant and free download. More Netbus 2.0 Server And Client videos. VNAP.NetBuster Proxy Pro is a GNU Licenced Freeware Proxy Server and Client. NetBus 2.0 Pro was released in. SMTP communication between mail servers. Remote Desktop Services - Wikipedia. Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2.
Vulnerability Description
Brief description: NetBus is a Trojan horse thatallows the installing user access to the system at a later time through the program.
Full description: NetBus allows the remote user to do most of the functionsBackOrifice can do(specifically, it allows anyone who knows the listening portnumber and Back Orifice passwordto remotely control the host. Intruders access the Back Orifice server usingeither a text or graphics based client. The Back Orifice server allowsintruders to execute commands, list files, start silent services,share directories, upload and download files, manipulate theregistry, kill processes, list processes, as well as other options).NetBusalso allows remote user to open/close the CD-ROM drive, sendinteractive dialogues to chat with the compromised system, listen tothe system's microphone (if it has one), and a few other features.
Components: none
Netbus 2 0 Server And Client Software List
Systems: Windows NT 3.5.1, 4.0;Windows 95, 98
Effect(s) of exploiting: This allows Administrator access to the target system.
Detecting the hole:
- For NetBus 1.53:
- Look for a file called SysEdit.exe with 473,088 bytes.(The file may have a different name, in which case lookfor the keys in the next section; one of them will either be,or have, the right name.)
- Check for the following registry keys:HKEY_CURRENT_USERSYSEDIT('SYSEDIT' will be the base name of the NetBus executable, so if thatis different this key will be too),HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUS, andHKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUSSettings.The keyHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun,may be added, in which case NetBus will run at boot time.(When NetBus is run, it needs to have the '/add' parametergiven to run at boot time.)
- Check if TCP ports 12345 and 12346 are open.The v1.53 server listens on 12345 for a remote clientand apparently responds via 12346.If they are,It will respond to a Telnet connection on port 12345 with its name and version number.
- Look for the file KeyHook.dll,most likely in the Windows directory.The v1.53 server requires this file for some of its functions.
- For NetBus 1.60:
- Look for a file called Patch.exe with 472,576 bytes.(The file may have a different name, in which case lookfor the keys in the next section; one of them will either be,or have, the right name.)
- Check for the following registry keys:HKEY_CURRENT_USERPATCH('PATCH' will be the base name of the NetBus executable, so if thatis different this key will be too),HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUS,HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUSSettings,andHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun.
- Check if TCP ports 12345 and 12346 are open.The v1.60 server listens on 12345 for a remote clientand apparently responds via 12346.If they are,It will respond to a Telnet connection on port 12345 with its name and version number.
- Look for the file KeyHook.dll,most likely in the Windows directory.The v1.60 server requires this file for some of its functions.


- For NetBus 1.70:
- Look for a file called Patch.exe with 494,592bytes.After configurationits size increases, usually by a couple of hundred bytes.(The file may have a different name, in which case lookfor the keys in the next section; one of them will either be,or have, the right name.)
- Check for the following registry keys:HKEY_CURRENT_USERPATCH('PATCH' will be the base name of the NetBus executable, so if thatis different this key will be too),HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUS,HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUSSettings,andHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun.
- Check if TCP ports 12345 and 12346 are open.The v1.70 server listens on 12345 for a remote clientand apparently responds via 12346.If they are,It will respond to a Telnet connection on port 12345 with its name and version number.Unlike the other two versions, the port numbersare configurable, so check other ports if this fails.The port can also be changed remotely.The response port is always the next-higher numbered port.
- Look for the file KeyHook.dll,most likely in the Windows directory.The v1.70 server requires this file for some of its functions.
- Look for the filesHost.txt and Memo.txt in the same directoryas the running server. If they exist, the NetBusa remote user has contacted the NetBus v1.70 server.
Fixing the hole:
- The steps to delete NetBus are the same for allversions, except that the file names of the executable differ.Also, v1.53 uses a dll, and v1.70 may create two text files.These should be cleaned out.
- Obtain the name of the NetBus server(most often SysEdit.exe).One way to do this is to goto the tasklist and kill any suspicous process. After each kill,try connecting to port 12345 and when that fails,the last task killed was the NetBus server.
- Next prevent NetBus from being started at boot time.Delete the registry keyHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRunXXX,where XXX is the name of the NetBus server.
- Delete the NetBus server executable.Also delete the KeyHook.dll file in the samedirectory as the NetBus server, if it is present.
- Restart the computer.
Other information: NetBus's protocol is not encrypted and the commands have a simple format:the name of the command, followed by a semicolon, followed by the argumentsseparated by semicolons. It is possible to set a password on the NetBusserver, and the password is stored in the registry as plaintext atHKEY_CURRENT_USERPatchSettingsServerPwd.There is a backdoor in NetBus that will allow anyone to connectwith no password. When the client sends the password to the server, it sendsa string similar to Password;0;my_password.If the client uses a 1 insteadof a 0, you will be authenticated with any password.
Keywords
Trojan horse,netbus
Netbus 2 0 Server And Client Software Update
Cataloguing
PA Classification(s):
Drivers ncr printers. RISOS Classification(s):
DCS Classification(s):

Netbus client (v1.70) works fine in Windows 2000 and in Windows XP as well. Major parts of the protocol, used between the client and server interaction (in version 1.70) are textual. Thus the server can be controlled by typing human understandable commands over a raw TCP connection. Download netbus server.exe for free. Internet & Network tools downloads - NetBus by Carl-Fredrik Neikter and many more programs are available for instant and free download. More Netbus 2.0 Server And Client videos. VNAP.NetBuster Proxy Pro is a GNU Licenced Freeware Proxy Server and Client. NetBus 2.0 Pro was released in. SMTP communication between mail servers. Remote Desktop Services - Wikipedia. Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2.
Vulnerability Description
Brief description: NetBus is a Trojan horse thatallows the installing user access to the system at a later time through the program.
Full description: NetBus allows the remote user to do most of the functionsBackOrifice can do(specifically, it allows anyone who knows the listening portnumber and Back Orifice passwordto remotely control the host. Intruders access the Back Orifice server usingeither a text or graphics based client. The Back Orifice server allowsintruders to execute commands, list files, start silent services,share directories, upload and download files, manipulate theregistry, kill processes, list processes, as well as other options).NetBusalso allows remote user to open/close the CD-ROM drive, sendinteractive dialogues to chat with the compromised system, listen tothe system's microphone (if it has one), and a few other features.
Components: none
Netbus 2 0 Server And Client Software List
Systems: Windows NT 3.5.1, 4.0;Windows 95, 98
Effect(s) of exploiting: This allows Administrator access to the target system.
Detecting the hole:
- For NetBus 1.53:
- Look for a file called SysEdit.exe with 473,088 bytes.(The file may have a different name, in which case lookfor the keys in the next section; one of them will either be,or have, the right name.)
- Check for the following registry keys:HKEY_CURRENT_USERSYSEDIT('SYSEDIT' will be the base name of the NetBus executable, so if thatis different this key will be too),HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUS, andHKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUSSettings.The keyHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun,may be added, in which case NetBus will run at boot time.(When NetBus is run, it needs to have the '/add' parametergiven to run at boot time.)
- Check if TCP ports 12345 and 12346 are open.The v1.53 server listens on 12345 for a remote clientand apparently responds via 12346.If they are,It will respond to a Telnet connection on port 12345 with its name and version number.
- Look for the file KeyHook.dll,most likely in the Windows directory.The v1.53 server requires this file for some of its functions.
- For NetBus 1.60:
- Look for a file called Patch.exe with 472,576 bytes.(The file may have a different name, in which case lookfor the keys in the next section; one of them will either be,or have, the right name.)
- Check for the following registry keys:HKEY_CURRENT_USERPATCH('PATCH' will be the base name of the NetBus executable, so if thatis different this key will be too),HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUS,HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUSSettings,andHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun.
- Check if TCP ports 12345 and 12346 are open.The v1.60 server listens on 12345 for a remote clientand apparently responds via 12346.If they are,It will respond to a Telnet connection on port 12345 with its name and version number.
- Look for the file KeyHook.dll,most likely in the Windows directory.The v1.60 server requires this file for some of its functions.
- For NetBus 1.70:
- Look for a file called Patch.exe with 494,592bytes.After configurationits size increases, usually by a couple of hundred bytes.(The file may have a different name, in which case lookfor the keys in the next section; one of them will either be,or have, the right name.)
- Check for the following registry keys:HKEY_CURRENT_USERPATCH('PATCH' will be the base name of the NetBus executable, so if thatis different this key will be too),HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUS,HKEY_CURRENT_USERNETBUSSettings,andHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun.
- Check if TCP ports 12345 and 12346 are open.The v1.70 server listens on 12345 for a remote clientand apparently responds via 12346.If they are,It will respond to a Telnet connection on port 12345 with its name and version number.Unlike the other two versions, the port numbersare configurable, so check other ports if this fails.The port can also be changed remotely.The response port is always the next-higher numbered port.
- Look for the file KeyHook.dll,most likely in the Windows directory.The v1.70 server requires this file for some of its functions.
- Look for the filesHost.txt and Memo.txt in the same directoryas the running server. If they exist, the NetBusa remote user has contacted the NetBus v1.70 server.
Fixing the hole:
- The steps to delete NetBus are the same for allversions, except that the file names of the executable differ.Also, v1.53 uses a dll, and v1.70 may create two text files.These should be cleaned out.
- Obtain the name of the NetBus server(most often SysEdit.exe).One way to do this is to goto the tasklist and kill any suspicous process. After each kill,try connecting to port 12345 and when that fails,the last task killed was the NetBus server.
- Next prevent NetBus from being started at boot time.Delete the registry keyHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRunXXX,where XXX is the name of the NetBus server.
- Delete the NetBus server executable.Also delete the KeyHook.dll file in the samedirectory as the NetBus server, if it is present.
- Restart the computer.
Other information: NetBus's protocol is not encrypted and the commands have a simple format:the name of the command, followed by a semicolon, followed by the argumentsseparated by semicolons. It is possible to set a password on the NetBusserver, and the password is stored in the registry as plaintext atHKEY_CURRENT_USERPatchSettingsServerPwd.There is a backdoor in NetBus that will allow anyone to connectwith no password. When the client sends the password to the server, it sendsa string similar to Password;0;my_password.If the client uses a 1 insteadof a 0, you will be authenticated with any password.
Keywords
Trojan horse,netbus
Netbus 2 0 Server And Client Software Update
Cataloguing
PA Classification(s):
Drivers ncr printers. RISOS Classification(s):
DCS Classification(s):
CVE Number: CAN-1999-0660 -- A hacker utility or Trojan Horse isinstalled on a system, e.g. NetBus,Back Orifice, Rootkit, etc.
Exploit Information
Attack:
Related Information
The NetBus program has two pages:a copyof the original page and a version called NetBus Pro.Advisories: CERT SummaryCS-99-01section 2, Back Orifice and NetBus;CIAC Information BulletinJ-032: Windows Backdoors Update II:(NetBus 2.0 Pro, Caligula, and Picture.exe)quoting ISS Vulnerability Alert#20,Windows Backdoors Update II: NetBus 2.0 Pro, Caligula, and Picture.exe.
Related Vulnerabilities:
Reportage
Reporting: Carl-Fredrik Neikter in (March 1998 )
Revision Number 1
Netbus 2 0 Server And Client Software Update
- Stacey Anderson (6/23/2000):
Initial entry
